- <!DOCTYPE html>
- Declares the document type and version of HTML, a required declaration.
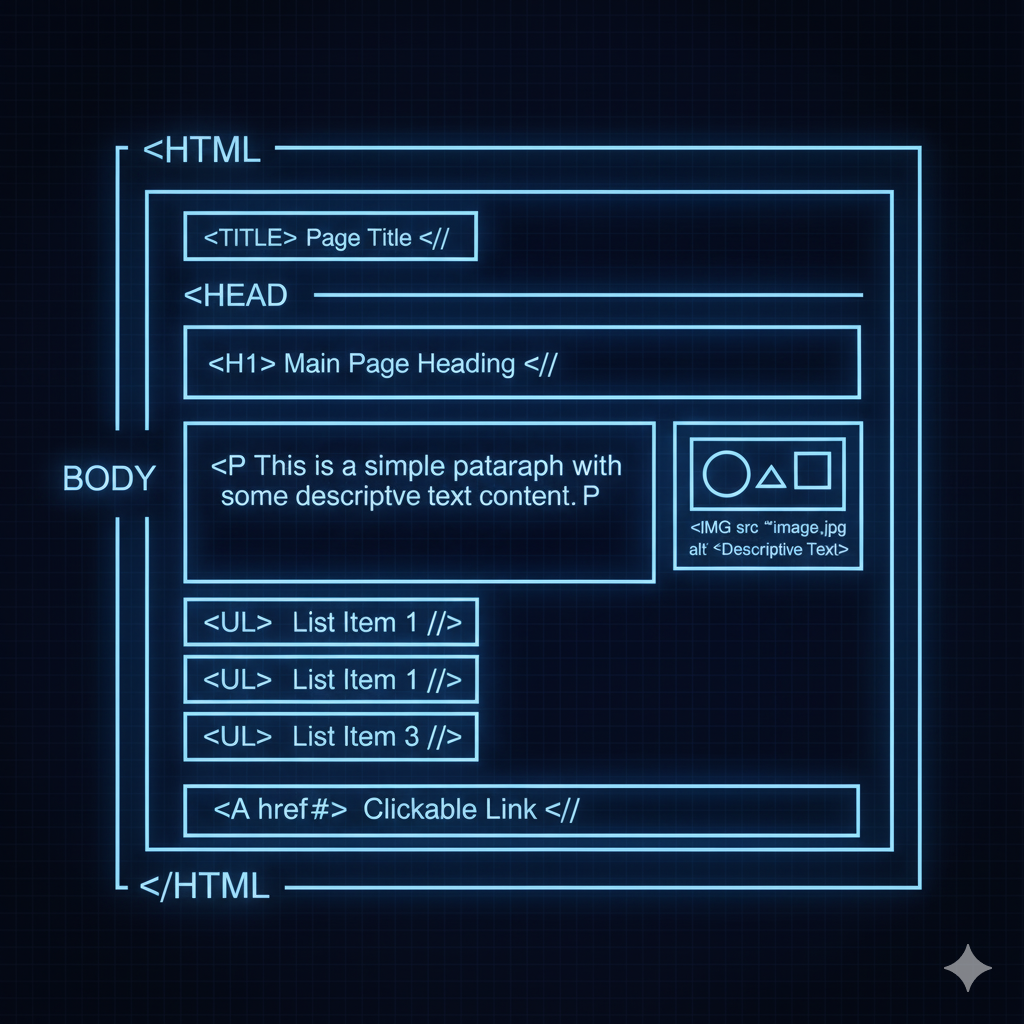
- <html>
- The root element that contains all the content of an HTML page.
- <head>
- A container for metadata about the HTML document.
- <title>
- Sets the title of the document, which appears in the browser tab.
- <body>
- Contains all the visible content of the page.
- <h1>
- Headings that define different levels of importance.
- <p>
- Defines a paragraph of text.
- <strong>
- Renders text with strong importance, usually bold.
- <em>
- Renders text with emphasis, usually italicized.
- <blockquote>
- Represents a section that is quoted from another source.
- <q>
- Defines a short inline quotation.
- <cite>
- Defines the title of a work, like a book or a song.
- <small>
- Renders text one font size smaller than the rest.
- <sub>
- Defines subscript text.
- <sup>
- Defines superscript text.
- <br>
- Inserts a line break.
- <hr>
- Creates a horizontal rule to separate content.
- <ul>
- An unordered list, typically with bullet points.
- <ol>
- An ordered list, typically with numbers.
- <li>
- A list item within an ul or ol.
- <table>
- Creates a table to display data.
- <tr>
- Defines a table row.
- <td>
- Defines a table data cell.
- <th>
- Defines a table header cell.
- <a>
- Creates a hyperlink.
- <img>
- Embeds an image.
- <picture>
- A container to provide multiple sources for an image, allowing the browser to choose the most suitable one.
- <audio>
- Embeds sound content.
- <video>
- Embeds video content.
- <iframe>
- Embeds another HTML document within the current one.
- <source>
- Specifies multiple media resources for video, audio, and picture elements.
